Thinking about future finances may be intimidating for most young people, but this introduction to investing makes it easy for anyone to understand the basics.
Source: Infographic: A Simple Introduction to Investing
In a previous infographic, we showed you that the compound interest is the most powerful force in personal finance. But how does a young person harness this incredible potential?
The answer: investing at an early age.
In this infographic, we clarify the difference between saving and investing, and give some basic tips on how to get started in the market.
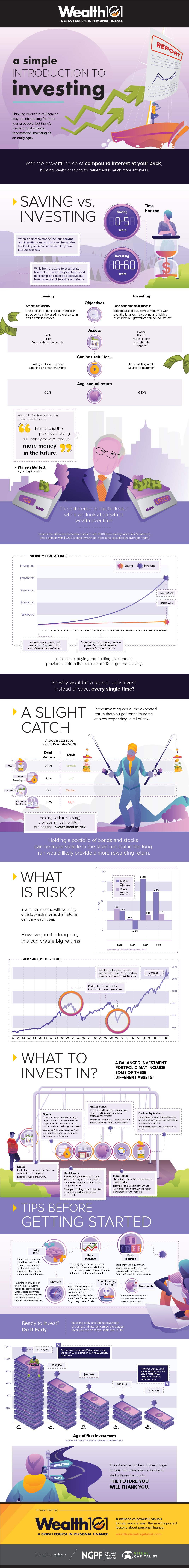
For many young people, the concepts of saving and investing blend together – after all, both are about accumulating more financial resources, right?
The terms can be used interchangeably in some cases, but they also have stark differences:
Saving
Saving is about safety and optionality over a short-term period (0-5 years). Cold hard cash can be saved to buy an important item, or to get through emergency situations.
Investing
Investing is about setting yourself up for long-term financial success. It’s the process of putting money to work over a long period, such as 10-60 years, by buying and holding assets that will grow from compound interest.
Investing is About Risk
In the investing world, the returns you get are linked to the perceived level of risk.
For example, holding onto cash is extremely low risk – and as a result, it has a low rate of return. Maybe you can earn 1% or 2% in a savings account, or using other short term cashlike instruments.
Meanwhile, if you buy stocks, they come with a certain level of risk. It’s possible the company you invest in may run into problems, or even go bankrupt – but for taking this extra risk, the market is willing to compensate you by paying a higher rate of return.
Investing is about taking advantage of higher rates of return and benefiting from the power of compound interest over long periods of time. It’s also about finding the best ways to mitigate the risk (diversification, being patient, etc.)